If complicated automotive brand automotive geaneology is your thing then Talbot is most assuredly the brand for you.

The name first appeared in Britain on French built Clément Bayard cars in 1905 taking the name from the British Charles Chetwynd-Talbot, 20th Earl of Shrewsbury who partenered Adolphe Clément-Bayard to sell his vehicles under the Clément-Talbot name before selling British assembled Clément Bayard’s which were sold as Talbot’s. In 1906 Talbot began selling British designs.
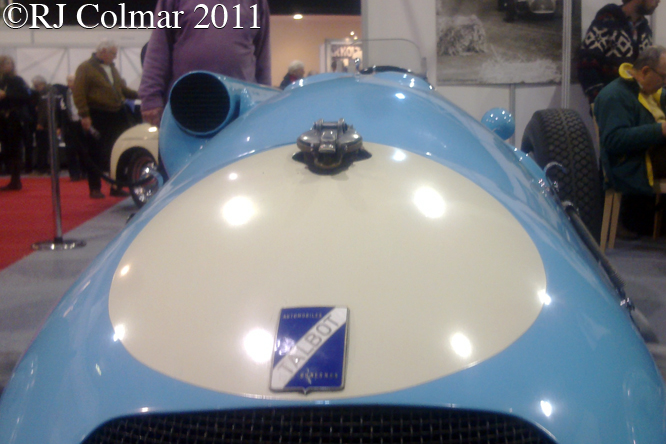

After The Great War of 1914/18 British owned French manufacturer Darracq took over the Talbot in 1919 marketing their products as Talbot-Darracqs. Another merger saw Talbot become part of the Sunbeam Talbot Darracq group in 1920 which became part of the Rootes Group in 1935. Antonio Lago acquired the French manufacturing facilities from the Rootes Group in 1935 and Talbot Lago continued production until 1960 when Simca who bought Talbot Lago in 1958 discontinued the brand.
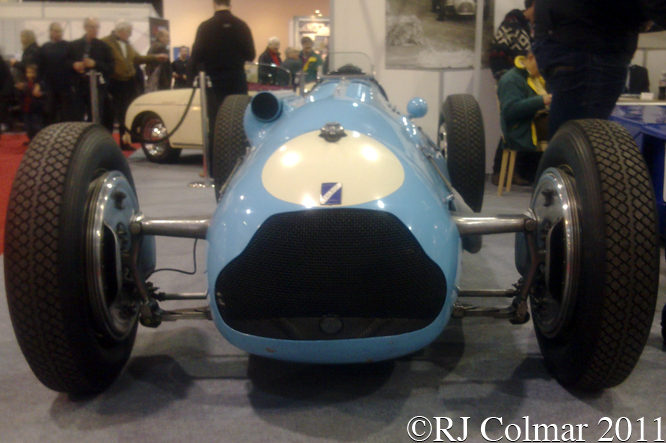

Antonio Lago was keen to use motor racing as a platform from which to promote his vehicles and with help from the Société d’Etude et de Fabrication d’Automobiles de Corse racing institution Lago started building two seat racing cars before building two six cylinder 4.5 litre /274 cui single seaters in 1937 with offset drivers seats. These cars were further developed in to a single seater car with a central seat that was driven by Raymond Mays, founder of ERA and later BRM, at Reims in 1939 where it retired with a split fuel tank.
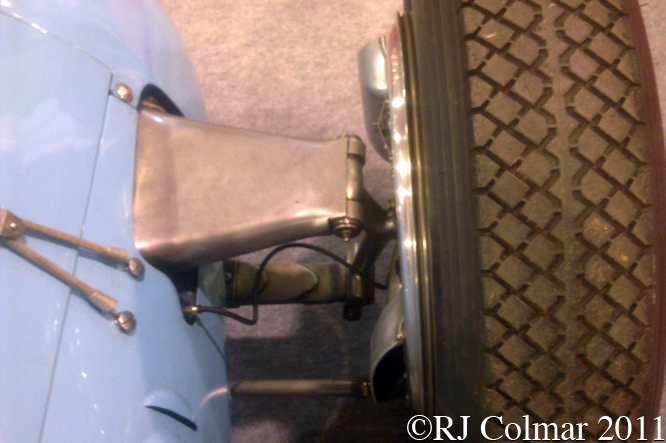

After the 1939/45 war a development of May’s car, which won the 1947 French Grand Prix with Louis Chiron at the wheel, would form the basis of today’s featured T26 C model of which twelve were built for clients to race.
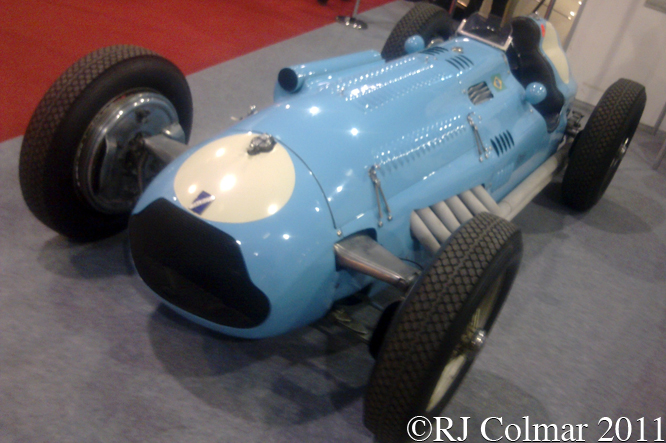

Despite racing against more sophisticated opposition particularly from Alfa Romeo who’s pre war supercharged 1.5 litre / 91.5 cui straight eight cars were still the most successful cars of the immediate post war era the Talbot Lago T26 C had reliability and fuel consumption in it’s favour in the longer races.
Averaging 9 miles per gallon compared to 2 – 3 mpg or worse for the supercharged cars meant that the Talbot Lago’s 200 plus horsepower was enough to cancel out the 100 hp advantage held by the more sophisticated machinery. The T26 C’s carried the road car Lago Record name on the side, some of the parts were interchangeable between the two models. The T26 C would be used as the basis for the Talbot Lago T26 GS sports cars one of which won Le Mans in 1950.
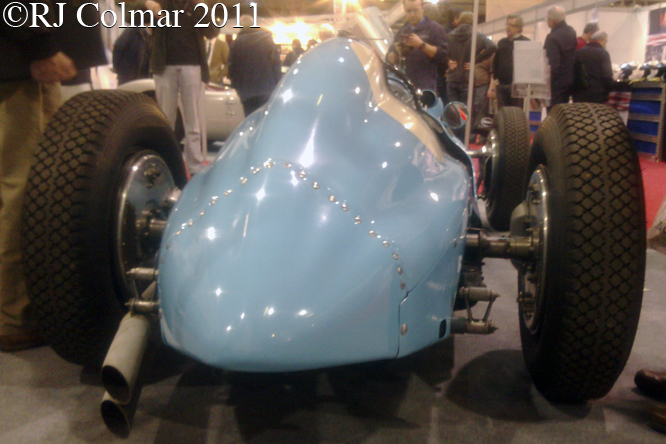

Chassis #110008 seen here was purchased by pre war racer Philippe “Phi Phi” Étancelin who drove the car to a second place finish at Albi in 1948, further second place finishes in the 1949 Italain, Czech and Pau Grand Prix with a season high win in the 1949 Paris Grand Prix.
At the Italian Grand Prix in 1950 “Phi Phi” aged 53, whose wife acted as his crew chief, became the oldest driver to score a point in the World Drivers Championship driving #110008.
#110008 was subsequently sold to Jean Achard a Frenchman resident in Brazil who intended to enter it in the Indy 500, before he was killed driving a Ferrari while competing in a hillclimb.
By the end of the ’50’s #110008 was raced by Brazilian Pinherio Pirres and later still was fitted with a Chevrolet motor and independent rear suspension. The car was brought back to the UK by Colin Crabbe in the late 70’s and restoration was completed while the car was owned by Tony Bianchi in the 1980’s.
My thanks to Tim Murray, hamsterace, Alan Cox, David McKinney, John Ruston and especially Tony “Odseybod” Turner who kindly sent me a copy of an article from September 2011 issue of Classic Cars about the T26C and T26 GS models.
Thanks for joining me on this “Phi Phi’s Parisian Winner” edition of ‘Gettin’ a li’l psycho on tyres’, I hope you will join me again tomorrow. Don’t forget to come back now !
PS My thoughts on the British Grand Prix can be found at Motorsports Unplugged on this link.

